Brief on AMIs
AMI (Amazon Machin Images) are used to build instances. They store snapshots of EBS volumes, permissions, and a block device mapping which determines how the instance OS controls the attached volumes.
AMIs can be shared, free or paid and can be copied across AWS Regions.
Type of AMI as per storage based
All AMIs are categorized as either backed by Amazon EBS or backed by instance store. The former means that the root device for an instance launched from the AMI is an Amazon EBS volume created from an Amazon EBS snapshot. The latter means that the root device for an instance launched from the AMI is an instance store volume created from a template stored in Amazon S3.
STEPS INVOLVED
Creating EC2 Instance whose AMI will be created
Choose EC2 service from AWS console and then click on Launch Instance
After choosing the option Launch Instance choose type of AMI to be launched for this example we are using Amazon Linux 2 AMI click on Select option.
 Option choose the opt
Option choose the opt
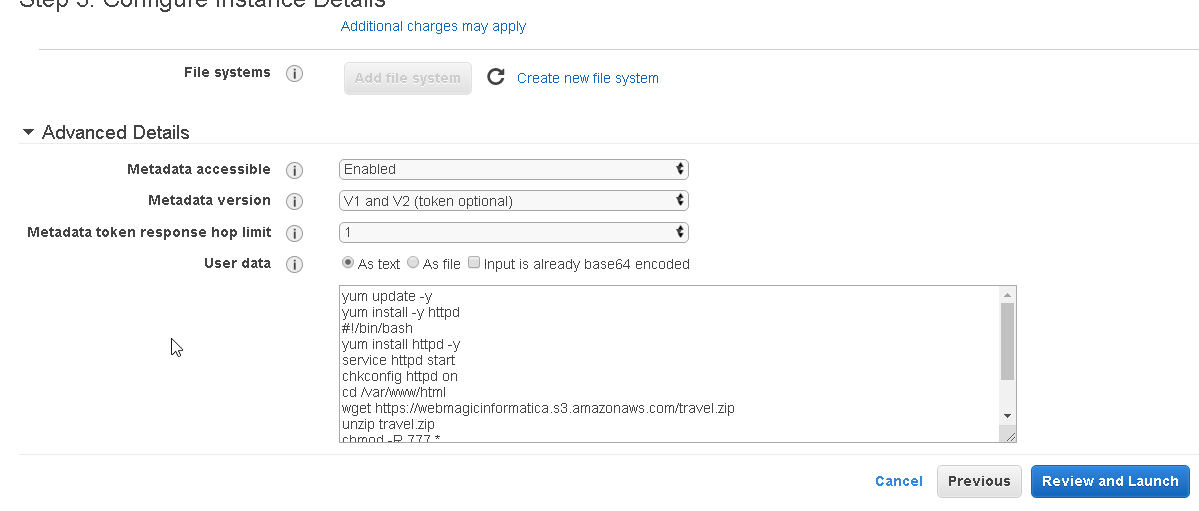
Click on next under this step we will add the script to install and configure httpd service and will install a sample static website.
This script we will provide under the User data option as shown.
Script can be copied from this GITHUB link :-
https://github.com/devops81/httpdsite/blob/master/script
After this click on Next and keep going to next step with required settings once reached on Security Group option we need to do following configuration changes.
Under the security group click on the option Add Rule and add http rule as showing below:-

http rule will allow browsing the httpd over the internet after this finally click on Review and Launch option and then finally on Launch option.
Once the instance is ready after launch we can see it under running instance panel and can connect to it using normal AWS procedure.

If we now copy the public IP of the running instance and paste it over browser we should be able to browse the httpd site which we deployed under User Data option while configuring the EC2 Instance.
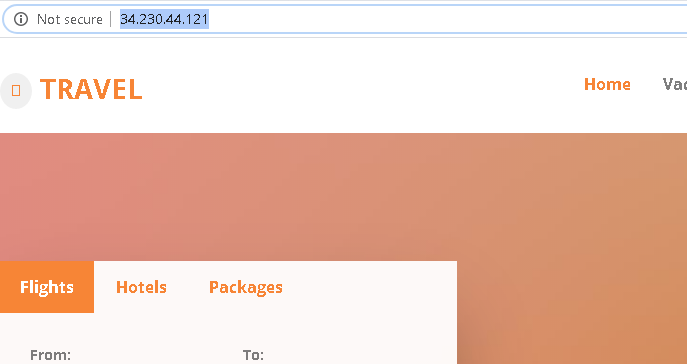
So till here we were successfully able to create a AWS EC2 instance with a bootstrapping option under the User data and as soon the instance is ready we were able to browse the httpd site which got configured during the startup of the EC2 instance.
Creating our custom AMI out of existing instance
Now as we have successfully create an instance with our site configured over it as a next step we want to create customized AMI image out of it so that we can launch new instances using this customized AMI.
Steps to create the AMI
Right click on the Instance which we created and then go to Image-> Create

Under the create image option choose the values appropriately and click on create image option.
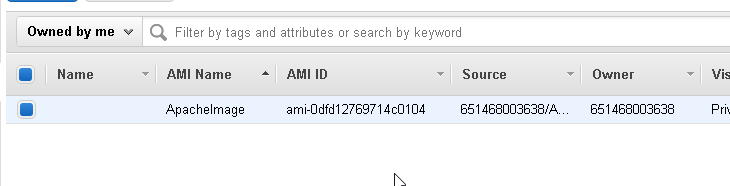
 After this if we go to AMI tab option under AWS console we should see the newly created AMI under the console.
After this if we go to AMI tab option under AWS console we should see the newly created AMI under the console.
Launching new AWS instance from customized AMI
Choose the AWS Launch Instance option from AWS console after this choose the My AMIs tab under Quick start opton the My AMIs tab should show the AMI which we have create just now in above steps.

Choose the AMI which we have created and click on select option after this keep selecting the option as we create normal new AWS instance under the security option we need to make sure that we have selected httpd inbound rule so that we can browse the httpd site over internet.

After we have selected all the required option under each step we can selection the Launch option.Once we have launched the new instance using the customized AMI we can see it under the AWS console.

Next we can try browsing the public IP of the newly create AWS instance it should take us to the httpd site.
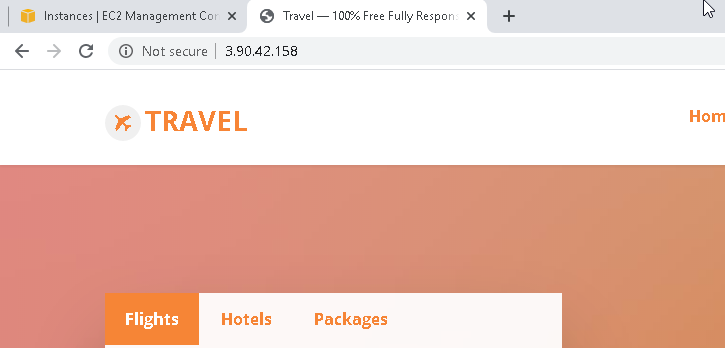
So this shows that we were successfully able to create customized AMI and then were able to spinup new instance from that particular customized AMI image.















































 Option choose the opt
Option choose the opt





 After this if we go to AMI tab option under AWS console we should see the newly created AMI under the console.
After this if we go to AMI tab option under AWS console we should see the newly created AMI under the console.